by DAVID BROWN | CLEARNFO.com | December 20, 2021
“We are looking at a winter of severe illness and death for the unvaccinated — for themselves, their families and the hospitals they’ll soon overwhelm” Joe Biden December 16, 2021
“The pandemic represents a rare but narrow window of opportunity to reflect, reimagine, and reset our world” – Professor Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman, World Economic Forum.
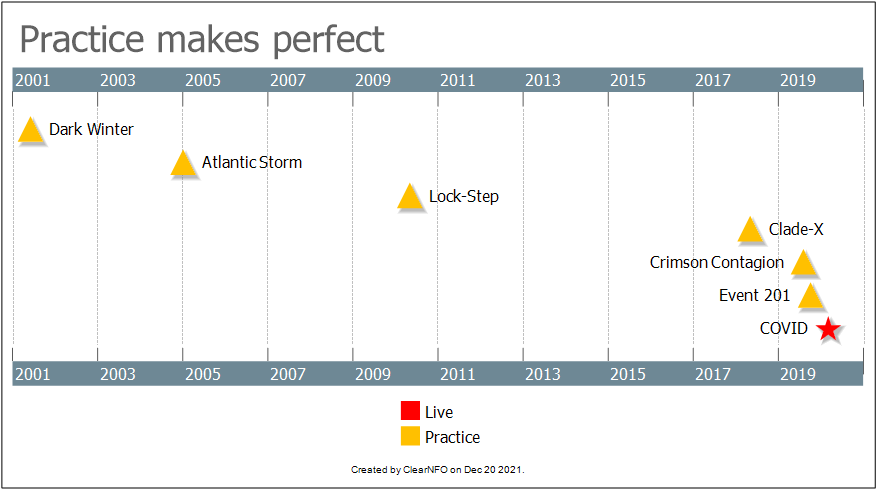
Theses are the ones not secrete, not behind closed doors.
OCTOBER 29, 2019: Universal Flu Vaccine
Health experts discussed the scientific and technological prospects of an effective universal influenza vaccine. Speakers included Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and Margaret Hamburg, former FDA commissioner. Panelists discussed the need for more funding for research, better collaboration between the private and government sectors, advances in technology in flu research and the goal of a universal flu vaccine.
October 18, 2019: Event 201
Event 201 was a 3.5-hour pandemic tabletop exercise that simulated a series of dramatic, scenario-based facilitated discussions, confronting difficult, true-to-life dilemmas associated with response to a hypothetical, but scientifically plausible, pandemic. 15 global business, government, and public health leaders were players in the simulation exercise that highlighted unresolved real-world policy and economic issues that could be solved with sufficient political will, financial investment, and attention now and in the future.
January to August 2019: Crimson Contagion
Crimson Contagion was a joint exercise conducted from January to August 2019, in which numerous national, state and local, private and public organizations in the US participated, in order to test the capacity of the federal government and twelve states to respond to a severe pandemic of influenza originating in China.
The simulation, which was conducted by the Trump administration’s Department of Health and Human Services in a series of exercises that ran from January to August 2019, involved a scenario in which a group of about 30 tourists returning from China spread a novel influenza A respiratory virus in the United States, beginning in Chicago. In less than two months the virus had spread from a single index case (a 52 year-old man returning to Chicago) to infect 110 million Americans; 7.7 million patients would require hospitalization, and 586,000 people would die from the novel virus. The 70-page report issued at the conclusion of the exercise outlined the government’s limited capacity to respond to a pandemic. States experienced “multiple challenges” requesting resources from the federal government “due to a lack of standardized, well-understood, and properly executed resource request processes,” the report said. Federal agencies lacked the funds, coordination, and capacities to implement an effective response to the virus.
May 15, 2018: Clade-X
Clade X is a day-long pandemic tabletop exercise that simulated a series of National Security Council–convened meetings of 10 US government leaders, played by individuals prominent in the fields of national security or epidemic response.
Drawing from actual events, Clade X identified important policy issues and preparedness challenges that could be solved with sufficient political will and attention. These issues were designed in a narrative to engage and educate the participants and the audience.
May 2010: Lock-Step Scenario (excerpt)
In 2012, the pandemic that the world had been anticipating for years finally hit. Unlike 2009’s H1N1, this new influenza strain — originating from wild geese — was extremely virulent and deadly. Even the most pandemic-prepared nations were quickly overwhelmed when the virus streaked around the world, infecting nearly 20 percent of the global population and killing 8 million in just seven months, the majority of them healthy young adults.
The pandemic also had a deadly effect on economies: international mobility of both people and goods screeched to a halt, debilitating industries like tourism and breaking global supply chains. Even locally, normally bustling shops and office buildings sat empty for months, devoid of both employees and customers.
The pandemic blanketed the planet — though disproportionate numbers died in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Central America, where the virus spread like wildfire in the absence of official containment protocols. But even in developed countries, containment was a challenge. The United States’ initial policy of “strongly discouraging” citizens from flying proved deadly in its leniency, accelerating the spread of the virus not just within the U.S. but across borders.
However, a few countries did fare better — China in particular. The Chinese government’s quick imposition and enforcement of mandatory quarantine for all citizens, as well as its instant and near-hermetic sealing off of all borders, saved millions of lives, stopping the spread of the virus far earlier than in other countries and enabling a quicker post-pandemic recovery.
China’s government was not the only one that took extreme measures to protect its citizens from risk and exposure. During the pandemic, national leaders around the world flexed their authority and imposed airtight rules and restrictions, from the mandatory wearing of face masks to body-temperature checks at the entries to communal spaces like train stations and supermarkets. Even after the pandemic faded, this more authoritarian control and oversight of citizens and their activities stuck and even intensified. In order to protect themselves from the spread of increasingly global problems — from pandemics and transnational terrorism to environmental crises and rising poverty — leaders around the world took a firmer grip on power.
At first, the notion of a more controlled world gained wide acceptance and approval. Citizens willingly gave up some of their sovereignty — and their privacy — to more paternalistic states in exchange for greater safety and stability.
Citizens were more tolerant, and even eager, for top-down direction and oversight, and national leaders had more latitude to impose order in the ways they saw fit. In developed countries, this heightened oversight took many forms: biometric IDs for all citizens, for example, and tighter regulation of key industries whose stability was deemed vital to national interests. In many developed countries, enforced cooperation with a suite of new regulations and agreements slowly but steadily restored both order and, importantly, economic growth.
By 2025, people seemed to be growing weary of so much top-down control and letting leaders and authorities make choices for them. Wherever national interests clashed with individual interests, there was conflict. Sporadic pushback became increasingly organized and coordinated, as disaffected youth and people who had seen their status and opportunities slip away — largely in developing countries — incited civil unrest. In 2026, protestors in Nigeria brought down the government, fed up with the entrenched cronyism and corruption. Even those who liked the greater stability and predictability of this world began to grow uncomfortable and constrained by so many tight rules and by the strictness of national boundaries. The feeling lingered that sooner or later, something would inevitably upset the neat order that the world’s governments had worked so hard to establish
January 14, 2005: Atlantic Storm
How would world leaders manage the catastrophe of a fast-moving global epidemic of deadly disease? Atlantic Storm was a ministerial table-top exercise convened on January 14, 2005 by the Center for Biosecurity of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, the Center for Transatlantic Relations of the Johns Hopkins University, and the Transatlantic Biosecurity Network. The exercise used a fictitious scenario designed to mimic a summit of transatlantic leaders forced to respond to a bioterrorist attack. These transatlantic leaders were played by current and former officials from each country or organization represented at the table. There was an audience of observers from governments on both sides of the Atlantic as well as from the private sector, but the venue was designed to focus all attention on the summit principals and their discussions around the table.
June 22-23, 2001: Dark Winter
The Dark Winter exercise, held at Andrews AFB, Washington, DC, June 22-23, 2001, portrayed a fictional scenario depicting a covert smallpox attack on US citizens. The scenario is set in 3 successive National Security Council (NSC) meetings (Segments 1, 2 and 3) that take place over a period of 14 days. Former senior government officials played the roles of NSC members responding to the evolving epidemic; representatives from the media were among the observers of these mock NSC meetings and played journalists during the scenario’s press conferences.
Softening up the terrain – Virus/pandemic movies flood the theaters 2001 – 2019:
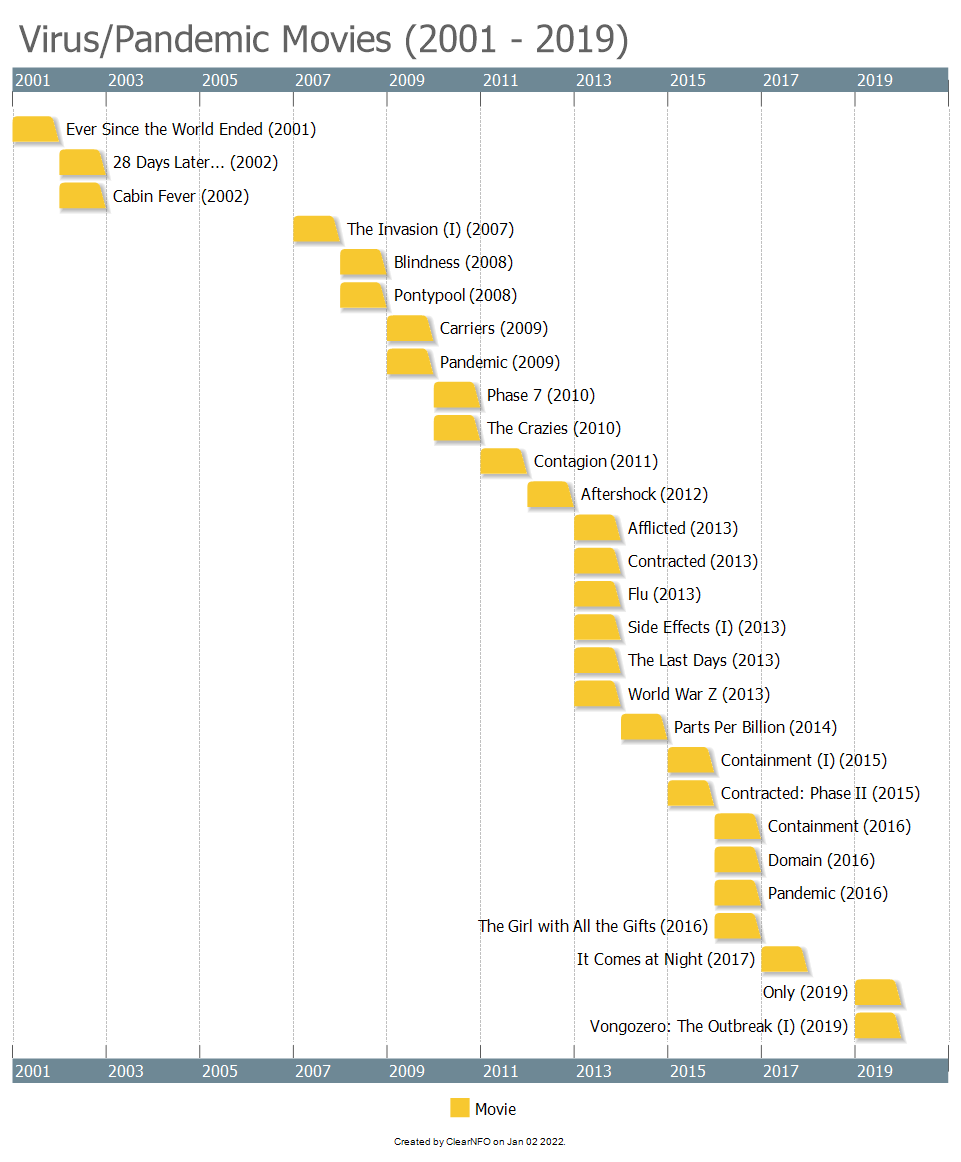
Also… The Andromeda Strain (1971) ; The Hot Zone (TV Series 2019) ;Contagion (2011); V for Vendetta (film) 2005
And more prep work …

SPARS Pandemic Scenario – Completed Projects Download document: SPARS Pandemic scenario book (PDF)
Posted June 3rd, 2022: THE PLAN – WHO plans for 10 years of pandemics, from 2020 to 2030
(Published May 4, 2022)
Contact: ClearNFO on MeWe, Gab, VK, Telegram, BitChute; or via email at ClearNFO@gmail.com